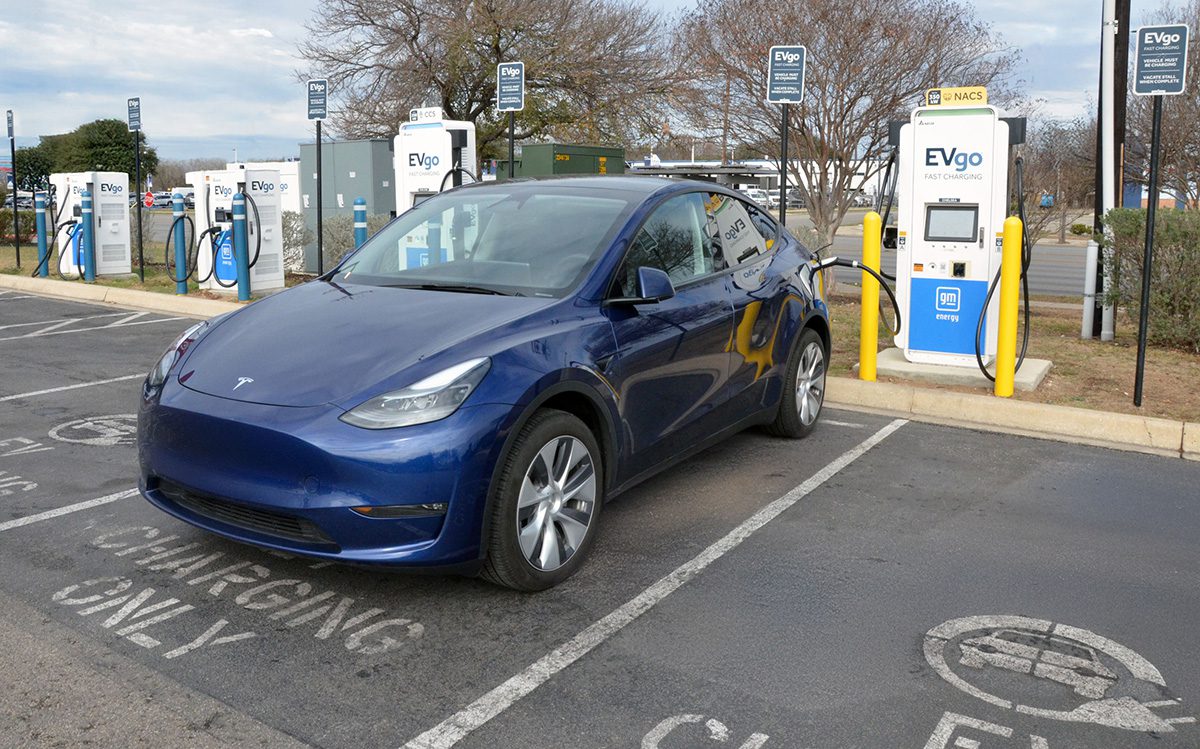
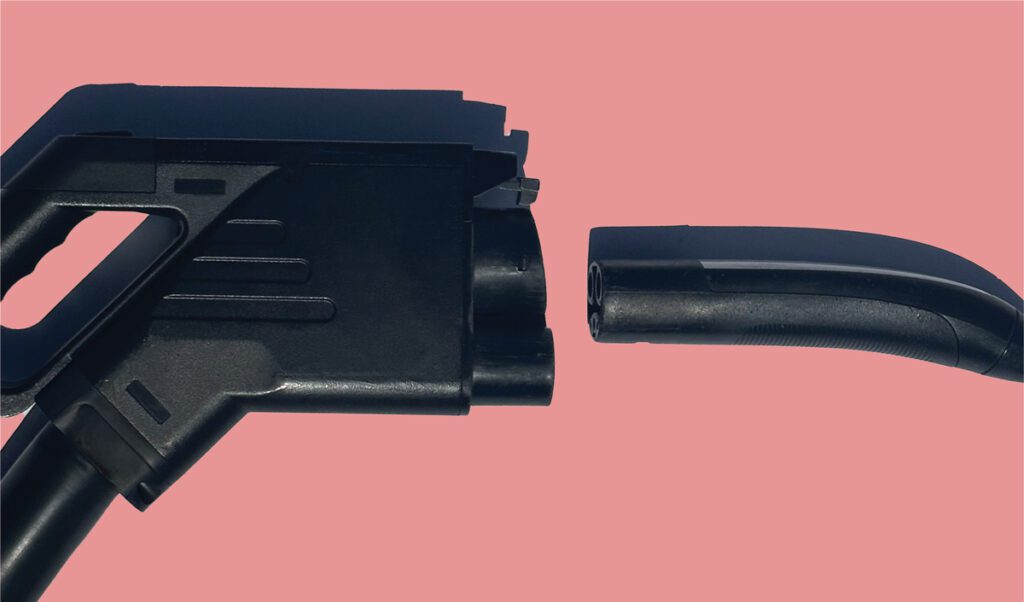
EVgo is expanding deployment of the North American Charging Standard (NACS) connectors across its public DC fast-charging network. After a 2025 pilot that installed nearly 100 NACS connectors across 22 major metropolitan areas, EVgo plans to accelerate deployment to reach more than 500 NACS connectors installed by the end of 2026, aiming to support rising demand from vehicles equipped with a NACS inlet.
EVgo says it will install NACS connectors at both existing and new sites, targeting both Tesla drivers and drivers of newer NACS-equipped EV models. The company expects that more than 80% of new EVs sold in North America will be NACS-compatible by 2030.
For 2026, EVgo says it intends to deploy additional NACS stalls in “key markets with increasing NACS vehicle penetration,” listing Austin, Houston, Las Vegas, Orlando, Phoenix, Chicago, Dallas, Detroit and San Francisco. Most sites are planned to include two to four NACS connectors, with the option to add more based on observed customer behavior and demand.
“We are already seeing an increase in NACS throughput on our network, and with more than 35 NACS models expected on American roads by the end of the year, we expect that to grow as we add more connectors throughout the country,” said Badar Khan, CEO of EVgo.
EVgo says drivers can enroll in Autocharge+ in the EVgo app to automatically start charging sessions at EVgo NACS locations without an adapter. EVgo also says most CCS (Combined Charging System) drivers can enroll in Autocharge+ as well, and that Autocharge+ has enabled over five million sessions on the EVgo network since its 2022 launch.
“Backed by rigorous testing at the EVgo Innovation Lab, we launched not only a market-leading product with our liquid-cooled NACS cables, but also a great customer experience by expanding Autocharge+ compatibility to serve both NACS and CCS drivers,” said Alex Keros, Senior VP of Product at EVgo.
Source: EVgo