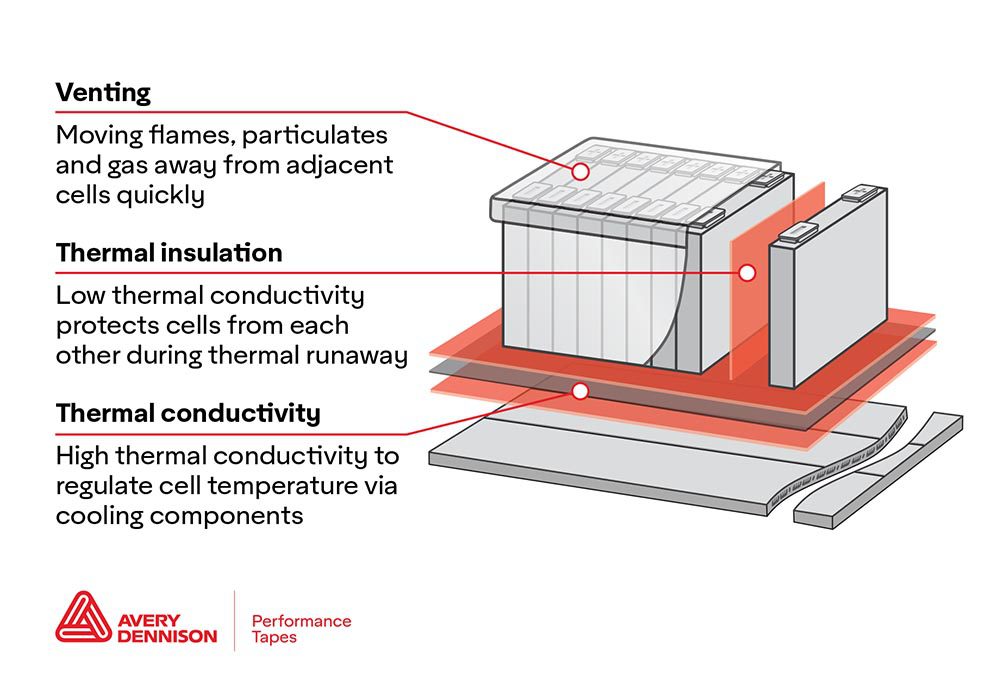
Freudenberg Sealing Technologies has expanded its material testing capabilities to include performance and compatibility evaluations of the rubber, elastomers and thermoplastics used to seal and safely maintain lithium-ion batteries. The company has installed equipment and adopted new testing protocols in its Plymouth, Michigan Central Laboratory that will provide data on which materials optimally resist breakdown from constant exposure to harsh electrolytic solutions.
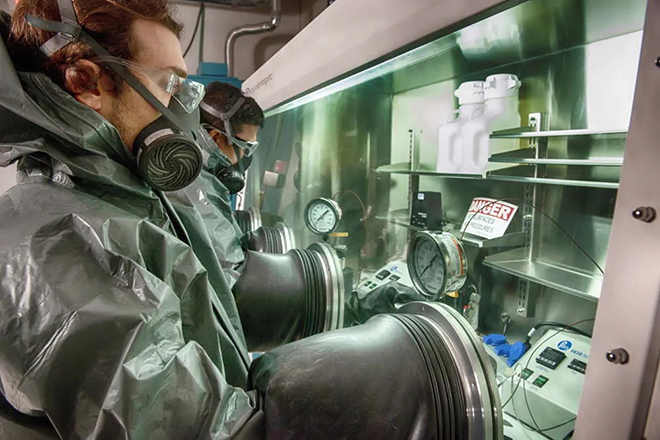
The centerpiece of the investment is a specially designed Isolation and Containment Chamber (IsoC) that allows technicians to safely conduct exposure testing using lithium electrolytic solutions, which are volatile, toxic and flammable when exposed to oxygen and ambient air moisture. The IsoC, a two-chambered glass and steel enclosure, allows chemists to work in a controlled, inert and moisture-free environment.
Freudenberg has also invested in a telemetry control system that facilitates remote IsoC monitoring, as well as protective gear, non-reactive immersion vessels and a safety monitoring and alarm system.
“What we can now offer customers is design security based on scientific data,” said R&D Director Joseph Walker. “Previous efforts have been conducted to determine the impact of materials on the electrolyte. This work focuses upon the impact the electrolyte has on the materials.”
Freudenberg will use two electrolytic solutions in its immersion testing: one that is commonly used in lithium-ion battery cells and one that has been manufactured as a control. The company will test families of materials, beginning with its own proprietary materials and then moving on to test commercially available substances.
Source: Freudenberg