Sponsored by Keysight Technologies
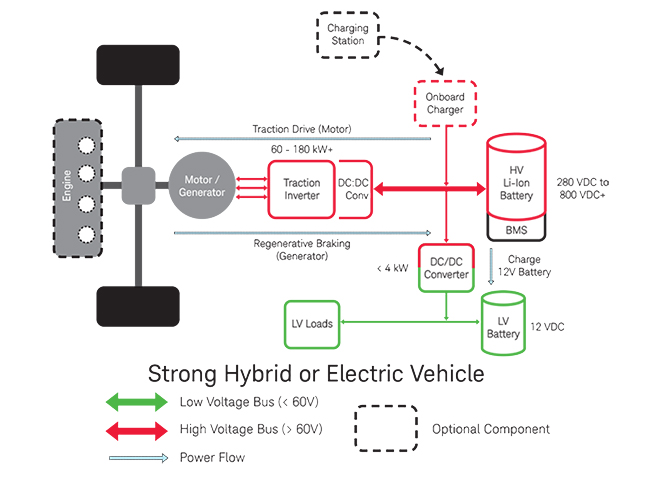
The DC-DC converter is a key component in hybrid and EV architectures, converting the higher voltage bus (MH – 48 V or EV/HEV – 100s of V) to the traditional 12 V power bus, from where most electrical loads are powered.
There is extreme downward cost pressure on design and test, across the DC-DC converter development life cycle. With silicon (Si) based power converter designs, most DC-DC converters are water cooled. The additional cooling design cost for the HEV/EV manufacturer is passed on to the design and test engineers, requiring reservoirs, pumps, and hoses to cool the DC-DC converter during design and test. So, manufacturers are minimizing the number of liquid-cooled modules by integrating multiple power converter applications into a single module (e.g. DC-DC converter+ Onboard Charger). In addition, designers are starting to adopt new power semiconductor technology by using Wide Bandgap (WBG) devices.
Download the new, free whitepaper from Keysight Technologies to learn more about the simulation, design, debugging, validation and manufacturing of DC-DC converters.