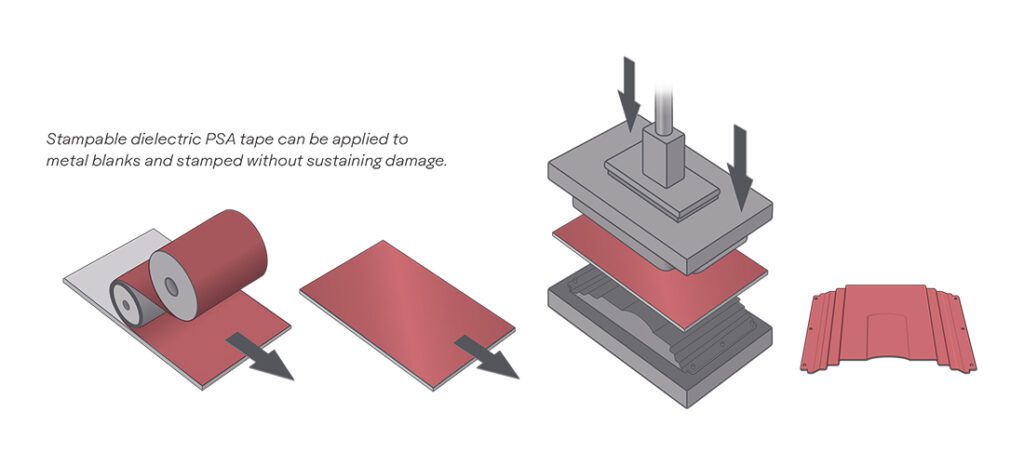
Solid-state electrolytes’ potential advantages in energy density and safety compared with conventional liquid electrolytes have made them the hottest topic in the battery world. However, there are several challenges to be overcome, including the low mobility of lithium ions in solid electrolytes. Now, a team of Stanford researchers have used ceramic nanowire fillers to enhance the ionic conductivity of polymer-based solid electrolyte by three orders of magnitude.
“Because of their low ionic conductivities at room temperature and poor electrochemical stability, solid polymer electrolytes have not been widely used in commercial lithium-ion batteries,” write Professor Yi Cui and his colleagues in the ACS journal Nano Letters.
“To address these concerns, previous approaches including cross-linking, using diblock copolymer, or adding plasticizers have been investigated. Unfortunately, these modifications diminish performance by loss of ionic conductivity and compatibility with lithium electrodes, and by deterioration of mechanical properties and flame resistivity. In contrast, dispersing ceramic particles in polymer matrix increases ionic conductivity effectively, meanwhile improving electrochemical stability and mechanical strength. The addition of these ceramic particle fillers is believed to hinder the polymer crystallization or to contribute highly conductive interface layers between polymer and ceramic.
“Nanoscale ceramic fillers have large specific surface area and can enhance the ionic conductivity drastically. Most research has emphasized ceramic nanoparticles, whereas little attention has been given to one-dimensional ceramic fillers. Here we explore nanowire fillers and demonstrate significant improvement of ionic conductivity and electrochemical stability.
“Our work opens the door for novel developments of one-dimensional Li+-conducting ceramic materials in solid electrolytes for lithium-ion batteries,” concludes the Stanford team.
Source: ACS journal Nano Letters via Green Car Congress