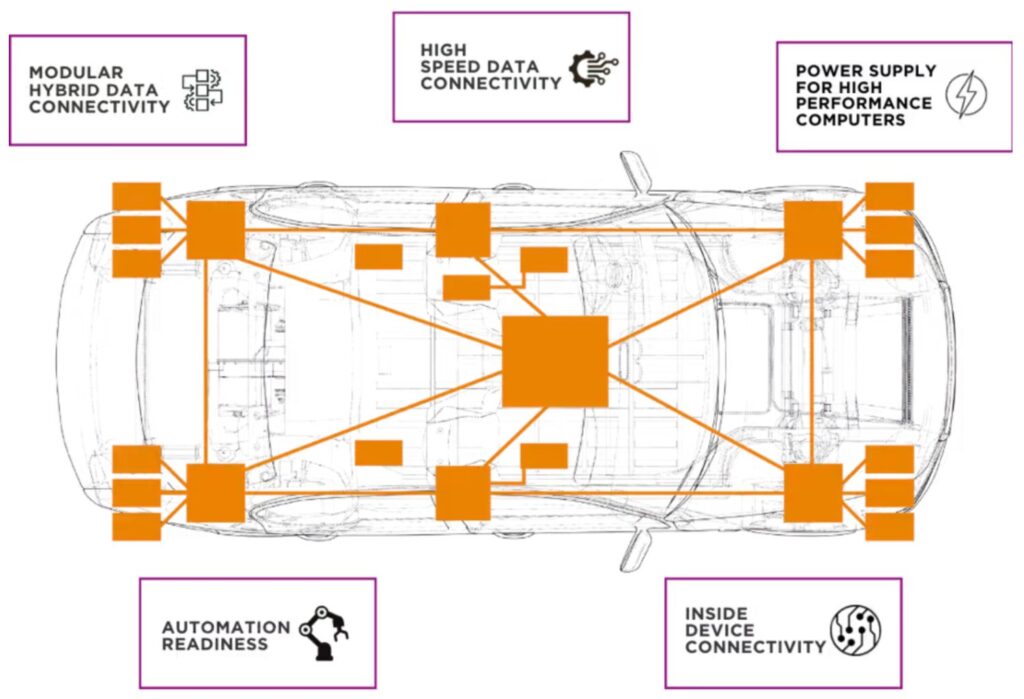
Researchers from The University of Tokyo claim to have successfully increased a lithium-ion battery’s voltage and its ability to suppress dangerous conditions that affect today’s batteries. Their paper is published in Nature Energy.
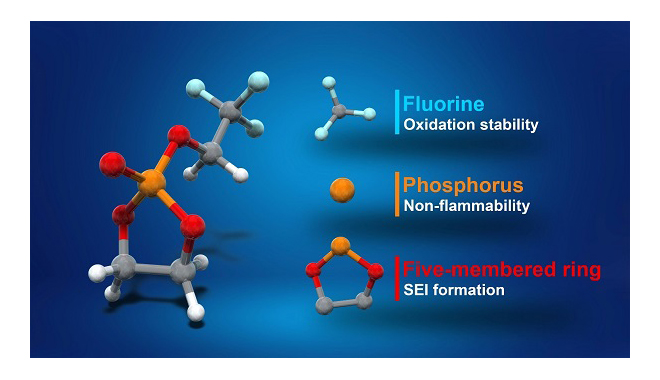
“A battery’s voltage is limited by its electrolyte material. The electrolyte solvent in lithium-ion batteries is the same now as it was when the batteries were commercialized in the early 1990s,” said Professor Atsuo Yamada. “We thought there was room for improvement, and we found it. Our new fluorinated cyclic phosphate solvent (TFEP) electrolyte greatly improves upon existing ethylene carbonate (EC), which is widely used in batteries today.”
EC is notoriously flammable and is unstable above 4.3 volts; TFEP, on the other hand, is nonflammable and can tolerate greater voltages of up to 4.9 volts. This extra voltage in an otherwise identically sized package leads to batteries with a higher storage capacity.
Source: The University of Tokyo