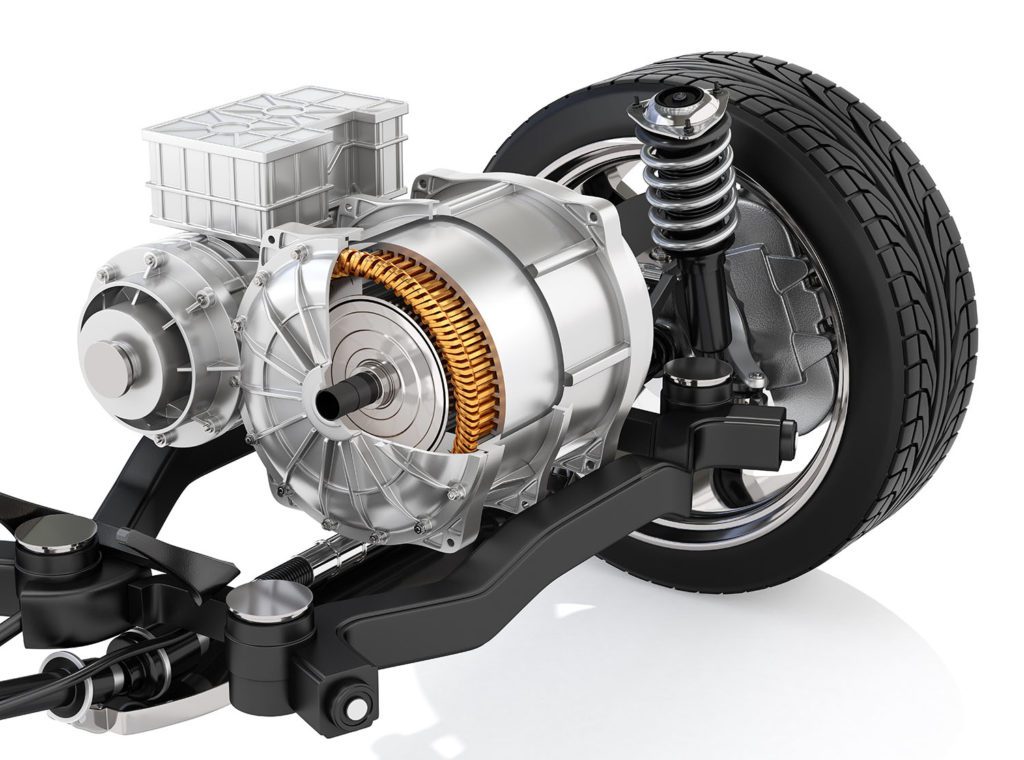
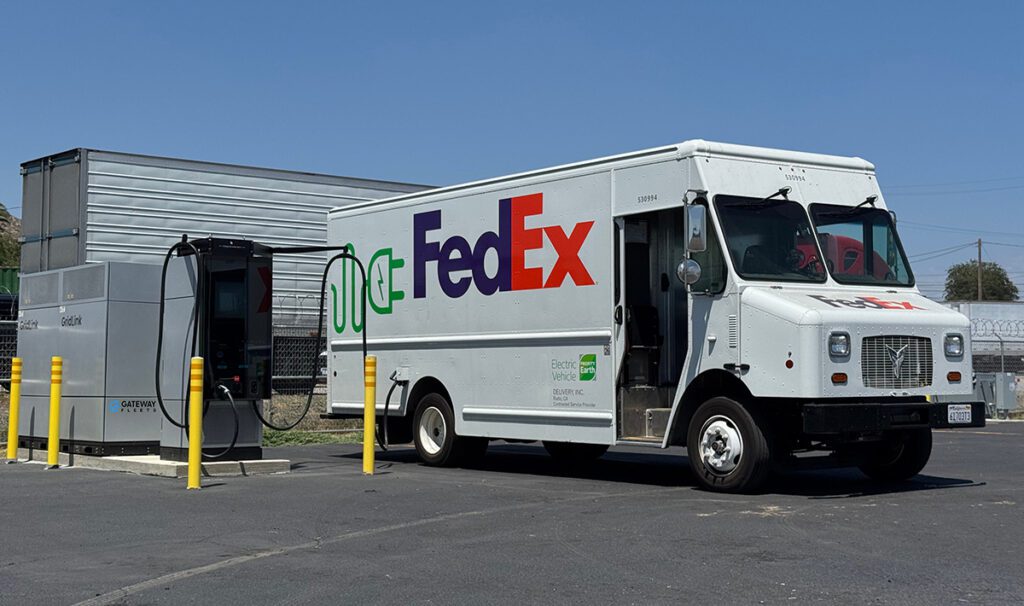
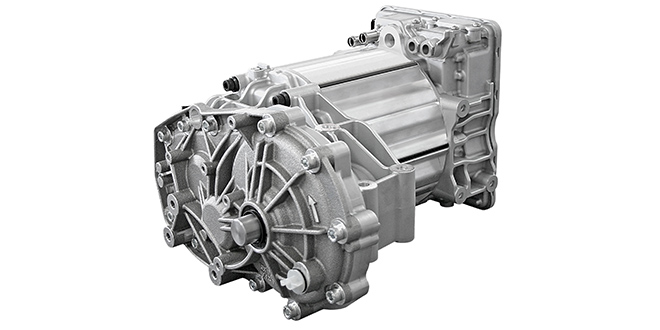
Auto parts giant Continental has developed a new electric powertrain especially for the Chinese market. The basic design for the new drive was created at Continental’s locations in Berlin and Nuremberg, and the specific customer applications were developed at Continental’s plant in China, where the system is produced in cooperation with Chinese suppliers.
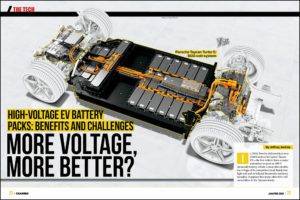
The new powertrain combines the electric motor, transmission, and power electronics in a single unit, eliminating many components such as connectors, cables, and hydraulic connections. Continental was able not only to achieve considerable cost savings, but also to reduce the weight of the drive by around 15 percent.
“Continental has proved its comprehensive expertise in electrified drives by means of numerous innovations, starting with its first series-production hybrid system in Europe in 2003,” said Dr. Bernd Mahr, head of Continental’s Hybrid Electric Vehicle business unit. “We have a profound understanding of the different technologies, and can therefore offer the right solution for every vehicle segment and market. And when we say ‘right,’ we mean a tailor-made technical solution that is suitable for the market and affordable. Thanks to its compact packaging, our new electric drive is not only lighter, but also more powerful than comparable concepts. This makes it fun to drive, which is an important factor in the acceptance of electric mobility.”
The compact system is scalable from around 60 to 120 kW, and can be used in a wide range of vehicles. It is available in two motor variants: an asynchronous machine (ASM) and a permanent-magnet synchronous machine (PSM).
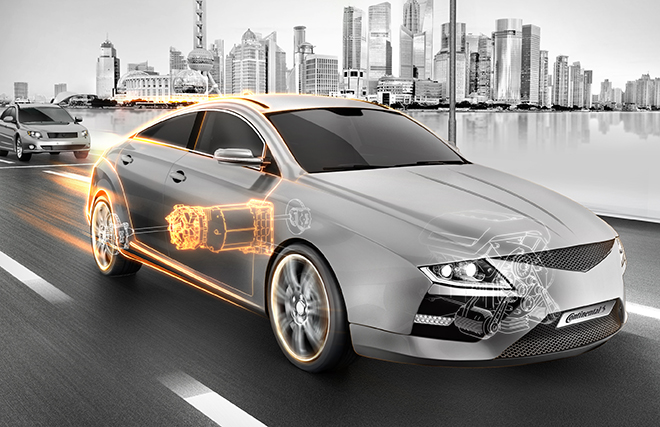

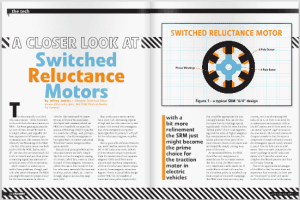
Most hybrid and electric vehicles use three-phase machines, in which the stator generates a rotating magnetic field that sets the rotor in motion. These may be asynchronous machines (ASM), or one of two types of synchronous machines: permanent-magnet synchronous machines (PSM), which have magnets on their rotors; and externally excited synchronous machines (SM), in which the rotor carries electromagnets in the form of excitation winding that is not magnetized until a flow of current is applied.
The asynchronous machine is suited primarily to smaller EVs due to its simple design. The compact and powerful permanent-magnet synchronous machine is preferred for use in larger EVs, as well as in plug-in hybrids.
“With the new, compact electric drive, we now have innovative solutions in our portfolio for all three motor technologies and can offer competitive tailor-made electrification for every vehicle type and every market,” explains Mahr. “Customers can assemble the best technology and output in accordance with the modular principle. The modular structure of the machine means that only the rotor and length vary depending on requirements.”
Source: Continental