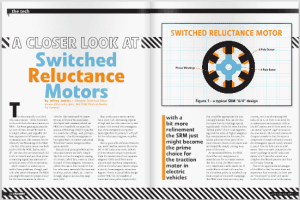
Among the many electrified vehicles on display at this week’s Geneva Auto Salon was one that demonstrates a new and possibly revolutionary energy storage system. Leichtenstein-based nanoFLOWCELL’s QUANT e-Sportlimousine, a sleek sports model with gull-wing doors, uses flow cell battery technology. Scientists at GE Global Research and Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory announced that they were working on a similar system last September.
Flow cells combine aspects of an electrochemical battery with those of a fuel cell. Liquid electrolytes—metallic salts in aqueous solution—are kept in two tanks and circulated through the cell. A membrane separates the two electrolytic solutions, but allows electrical charge to pass through and produce power.

“The advantages of the nanoFLOWCELL lie in its high charge density, high performance density, and its light weight compared to conventional energy storage systems,” explains Nunzio La Vecchia, Technical Director of nanoFLOWCELL. “Furthermore, it contains no harmful substances, no moving parts, and it is very efficient.”
According to the company, its system achieves continuous output of 30 kW at a nominal voltage of 600 V and 50 A, and offers specific energy five times better than that of current lithium-ion technologies. The company also claims its flow cells can go through 10,000 charging cycles with no noticeable memory effect.

The QUANT e-Sportlimousine prototype has two 200-liter (53-gallon) tanks on board, for a total energy capacity of 120 kWh. The company says the vehicle has a range of between 400 and 600 km (249-373 miles), and that it would be possible to increase the tank volume to 800 liters.
There’s one major drawback to current flow cell technology – once the electrolytic fluids are discharged, the contents of both tanks must be replaced. The prototype features dual filler necks, one for each electrolyte.
The QUANT uses four electric motors (120 kW continuous, 170 kW peak per unit) for all-wheel drive with torque vectoring, and two supercapacitor banks for energy storage.
The company is planning on producing four drivable prototypes in 2014.
Source: nanoFLOWCELL AG, Green Car Congress