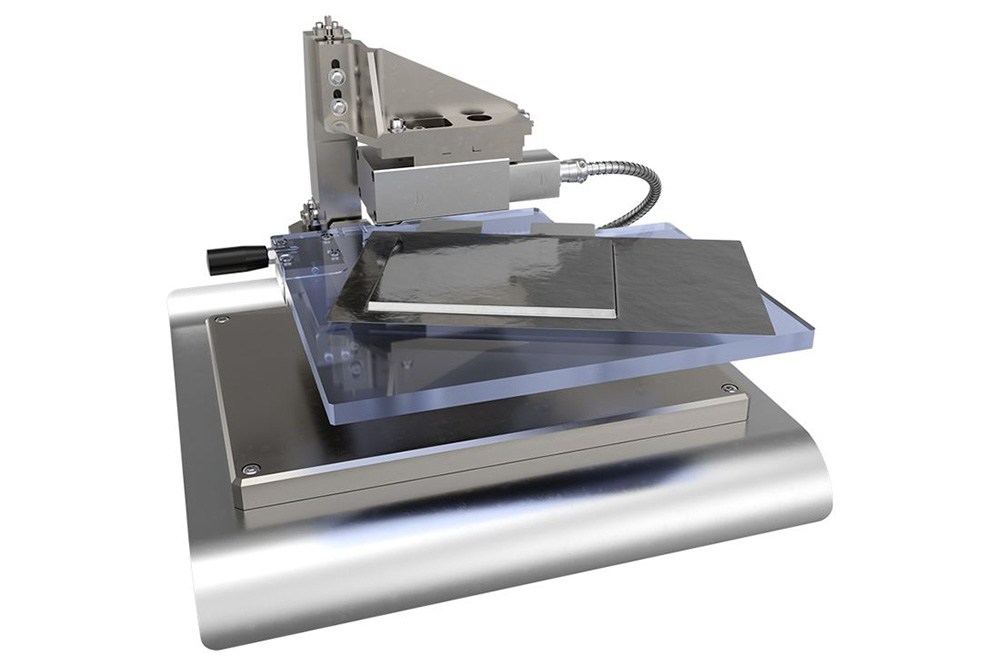
Marposs, a designer and manufacturer of measurement, inspection and testing products, has announced a new system for checking the welding joints of pouch cell batteries within the production process, consisting of interferometric sensors and the company’s NCG (non-contact gauge) controller.
The system works by splitting light into two beams that travel different optical paths and are later combined to produce interference, which can identify refractive changes and surface irregularities.
Pouch cell batteries are typically sealed using impulse or contact welding (heat sealing), which fuses the plastic layers together. The thickness of this joint is a key indicator of the quality of the seal, and must be measured while the material is still soft. Marposs says its system is able to check the thickness right after the welding process using the non-contact interferometric technology.
The solution can measure thin external plastic layers starting at 1 µm and accommodate thickness variations due to the presence of the tabs in parts of the welding seam. It comes with a measuring snap with two interferometric sensors that enable the simultaneous measurement of the total thickness of the welding seam and the thickness of the two external plastic layers. Each sensor has a measuring field of 900/1.8 mm and offers a repeatability range within 1 mm of the application thickness.
Source: Marposs