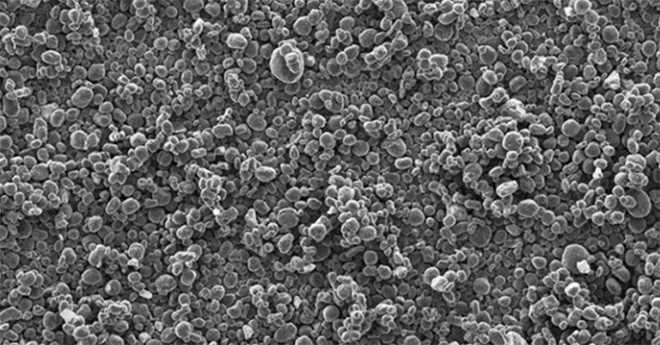
Graphite mining and product company Ceylon Graphite has announced test results for its silicon-enhanced vein graphite anode material. In independent tests performed by Warwick University, Ceylon’s silicon-enhanced vein graphite yielded a specific discharge capacity (SDC) of 446 mAh/g in comparison to vein graphite’s typical SDC of 393 mAh/g. Ceylon’s 13% higher SDC was achieved in vein graphite with a core-shell silicon additive.
According to Ceylon Graphite, the higher SDC is the result of many factors, including the additive, proprietary silicon enhancements, the high crystallinity of vein graphite and the high purity of vein graphite.
“In addition, we believe that the energy consumption of the end-to-end process of producing battery grade anode material from vein graphite is the lowest, relative to synthetic and flake graphite, because vein graphite from Sri Lanka does not require primary processing, due to the high in situ grade above 90% Cg,” said Ceylon CEO Don Baxter.
Source: Ceylon Graphite