The European Association of Automobile Manufacturers (ACEA) has published an interactive map that illustrates the correlation between the adoption of plug-in vehicles (which the organization, apparently feeling that the industry needs yet more acronyms, refers to as “electrically-chargeable vehicles,” or ECVs) and per-capita GDP.
The ACEA reports that plug-in vehicles accounted for 3.0% of all new cars registered in the EU in 2019. The market has grown significantly this year—according to EV Volumes, in the first half of 2020, plug-in sales in Europe grew by 57%, while the overall vehicle market declined by 37%. EV Volumes expects to see monthly market shares of 7-10% for the rest of the year. (The ACEA’s figures include only the 27 EU member states and the UK—they do not include EV sales leader Norway, where plug-in vehicles accounted for 68% of new car sales in H1 2020, or number-two Iceland, which reached 49%.)
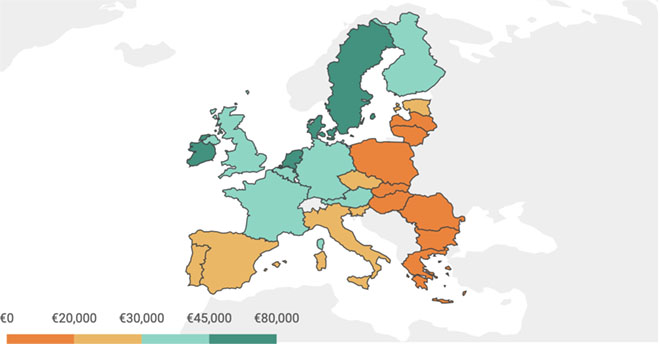
Unsurprisingly, the ACEA finds that the market uptake of plug-in vehicles has been directly correlated with each country’s GDP per capita, showing that “affordability is a major barrier to consumers.”
Almost 80% of EU plug-in sales in 2019 were concentrated in six Western European countries, which also had some of the highest GDPs in the economic bloc.
The plug-in shares in the five largest EU and UK auto markets were:
- United Kingdom—3.1% (GDP of €37,780)
- Germany—3.0% (GDP of €41,510)
- France—2.8% (GDP of €35,960)
- Spain—1.4% ECVs (GDP of €26,440)
- Italy—0.9% (GDP of €29,610)
Eleven of the EU member states had a plug-in market share lower than 1%. All of these had a per-capita GDP below €30,000.
The least charged EU country was Estonia, which had a plug-in vehicle market share of only 0.3% (and GDP of €21,160) in 2019. Ironically, back in 2013, Estonia was one of the first countries to encourage EV adoption. As Charged reported, the Baltic nation installed a DC charging network that was by far the most extensive in Europe, and was rivaled in coverage only by Japan.
Source: ACEA via Green Car Congress