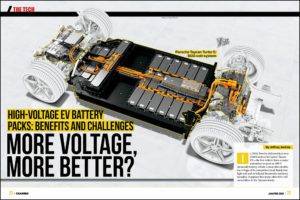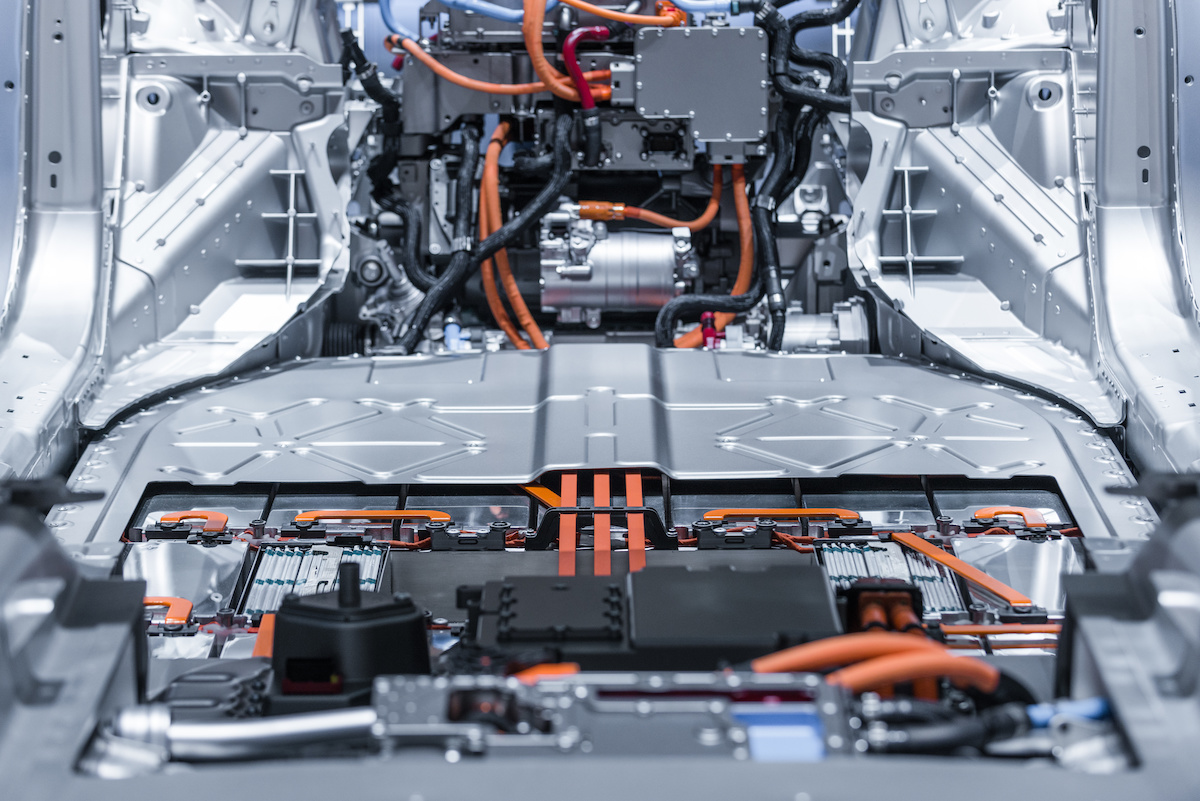
Many power electronics today are being designed for use in high-temperature, high-voltage environments, such as inside electric vehicles (EVs). However, size, weight, and power (SWaP) are also key factors driving electronic product development. These conflicting design criteria are an issue for many electrical engineers because space is not available to simply add a cooling system, as this will add weight and increase the product’s overall footprint. Therefore, many of these electronic components are susceptible to “running hot” at the high temperatures and high voltages used in these tiny spaces.
Given the challenges for EV components, it’s critical for designers to select the right high-voltage, high-temperature capacitors to meet application requirements and industry certifications. We’ll review how reducing losses in a DC-to-DC (or DC/DC) converter, the converter (and overall vehicle) benefits from improved energy efficiency, a more streamlined design, and diminished heating from components; how capacitor characteristics impact temperature rise and reliability; and how low loss, ultra stable high-capacitance MLCCs can optimize power electronics.
Ultimately, the more efficiently power is converted, the further distance the EV can travel on one charge. Learn more about choosing the right capacitors to operate reliably and efficiently, even in the most demanding EV applications.