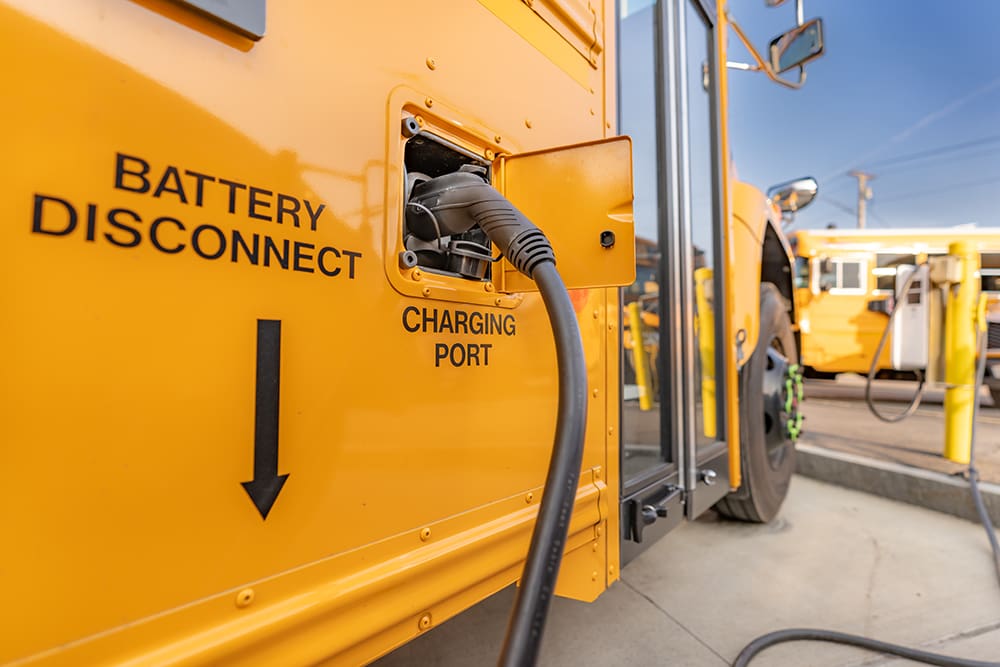
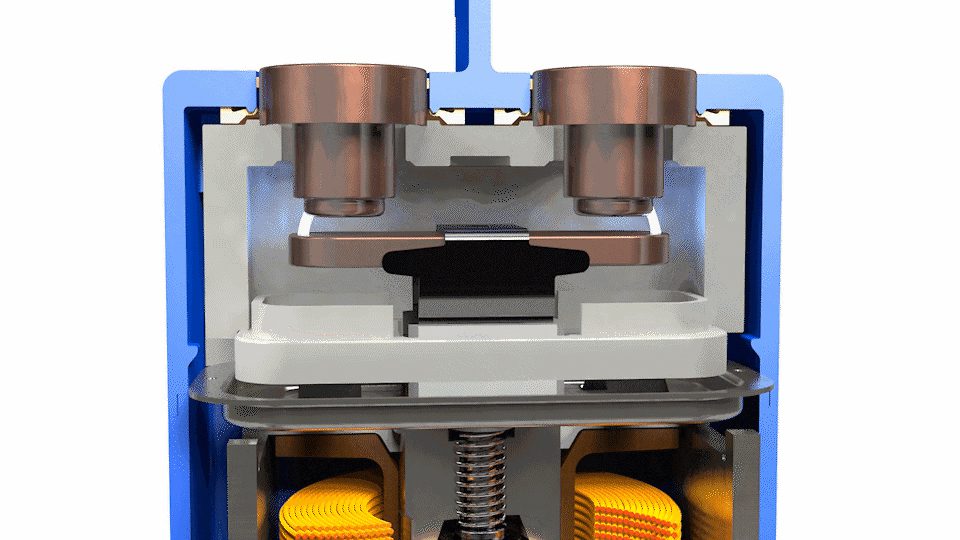
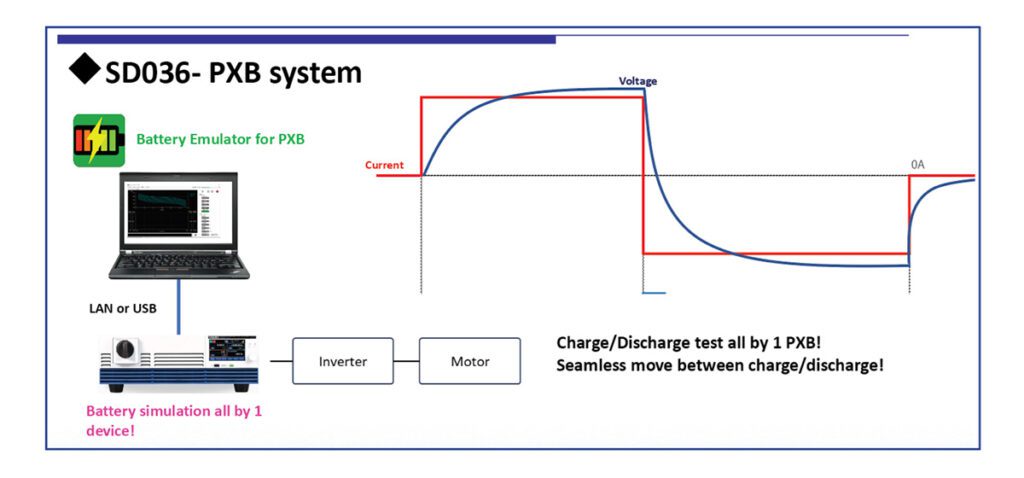
In a recent interview with Charged, Matt Reynolds from TDK provided a detailed look into the role and design of high-voltage DC contactors used in electric vehicles. These vital safety devices manage the connection and disconnection between the battery and other high-voltage systems like the inverter or charging port. Most EVs use at least four contactors strategically placed within the battery disconnect unit to control current flow during charging and operation.
During the conversation, Reynolds explained the importance of contact resistance in determining a contactor’s efficiency and current-carrying capacity. Lower contact resistance reduces heat buildup, which is essential for maintaining safe operating temperatures—especially when handling up to 500 amps of continuous current. He also noted that contact resistance can shift slightly over time due to arcing during current-breaking events, but TDK’s design ensures long-term reliability.
The interview also covered the construction of TDK’s contactors, specifically their use of a ceramic switching chamber that is hermetically sealed. This chamber is filled with a custom gas mixture designed to quench electrical arcs and maintain performance over time. Reynolds emphasized that this approach, rooted in TDK’s long history with gas discharge tube technology, offers better lifetime performance and reliability than resin-sealed alternatives.
Reynolds explained coil design options, comparing TDK’s dual coil system with pulse-width modulation (PWM) approaches. The dual coil method uses higher power briefly to close the contact, then switches to a lower power to hold it, offering energy savings without the EMI concerns sometimes associated with PWM. This makes it a clean, efficient solution for EV applications.
To learn more, watch TDK’s recent webinar:
Optimizing EV Safety And Efficiency With The Right High Voltage Contactor
And visit TDK’s High-Voltage Contactors site here.