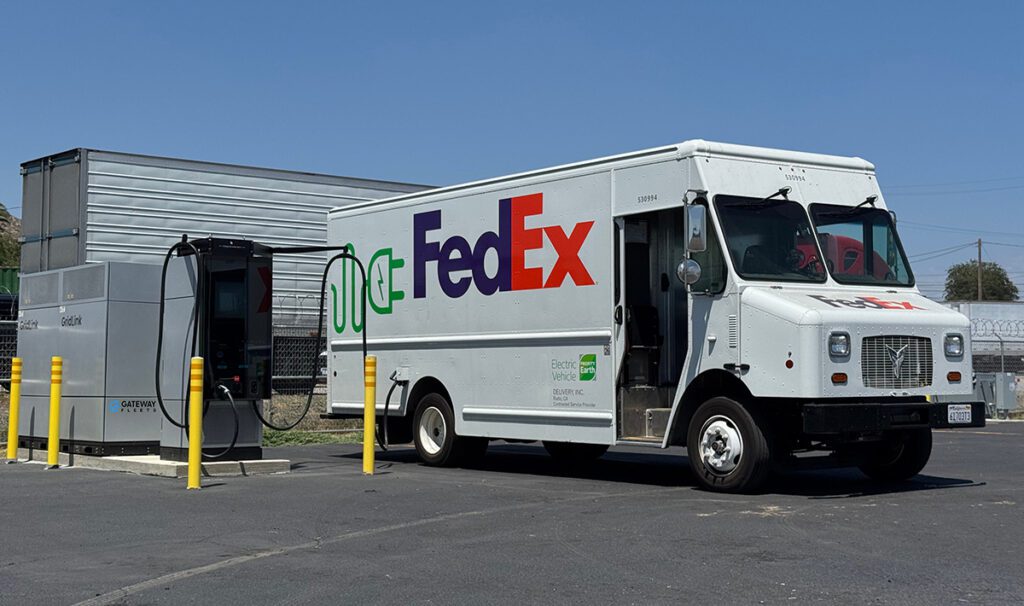
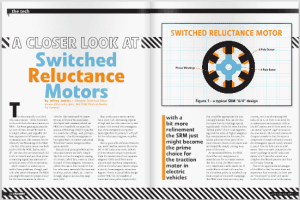
Nissan has introduced a fully automated vehicle towing system at its Oppama Plant in Japan. The Intelligent Vehicle Towing (IVT) system uses a modified LEAF with autonomous capability to tow trollies carrying finished vehicles between loading and unloading points at the plant.
The plant’s existing logistics system uses human drivers to transport finished vehicles from the end of the production line to a wharf to be loaded onto ships.
Unlike conventional guided vehicle systems for transporting parts, which often require rails or magnetic tape, the IVT system needs no special infrastructure. The towing car is equipped with an array of cameras and laser scanners that detect lane markings, curbs and potential obstacles. By cross-referencing this information with map data, the towing car calculates its own location and negotiates the route to its destination unaided.
The towing route can easily be altered to accommodate changes in production processes. All driverless towing cars are connected to a traffic control system, which can monitor the location, speed and remaining battery charge of each vehicle. A fail-safe system is in place to counter risks such as adverse weather and low light conditions.
Trial operations of the system began a year ago, and more than 1,600 test runs have been carried out.
Source: Nissan