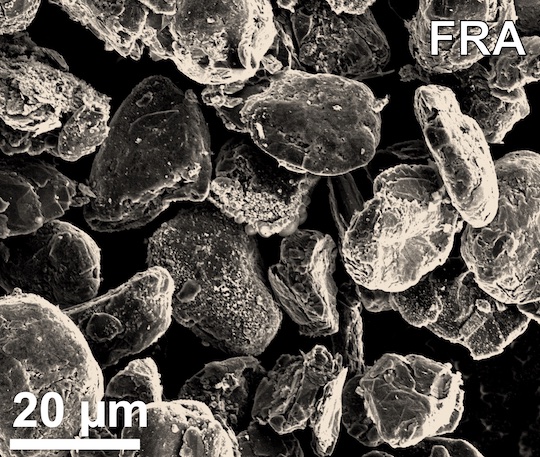
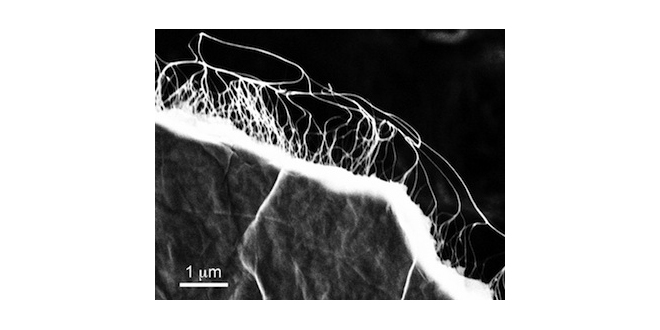
Rice University scientists have reported what they believe to be a partial solution to the mounting disposal problem of worn-out lithium-ion batteries. It relies on a unique “flash” Joule heating process they have developed to produce graphene from waste. The lab of Rice chemist James Tour is said to have reconfigured the process to quickly… Read more »
Search Results Found For: ""rice university""
New analytical model from Rice University helps fine-tune battery performance
Rice University engineers have devised a simpler and more efficient way to predict battery performance, which they claim is 100,000 times faster than current modeling techniques. The analytical model developed by materials scientist Ming Tang and graduate student Fan Wang of Rice University’s Brown School of Engineering doesn’t require complex numerical simulation to guide the… Read more »
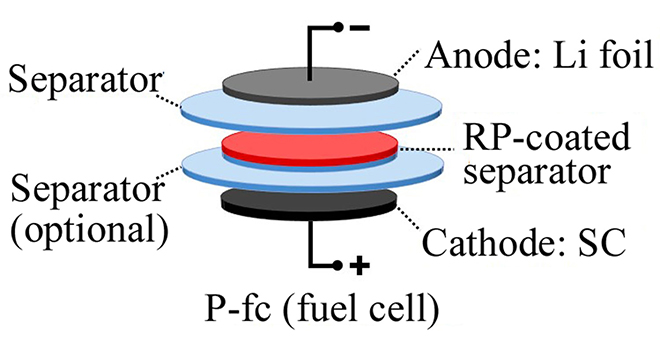
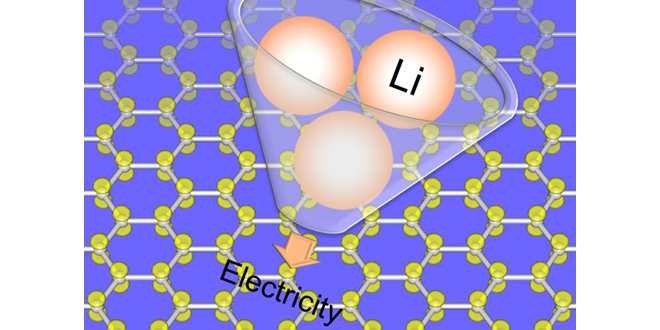
Rice University adds red phosphorus to separators to foil dendrites
Rice University scientists have found that adding a layer of red phosphorus to separators in lithium metal batteries can signal when damaging dendrites threaten to create a short circuit. Rice University chemist James Tour made lithium metal test cells with a coat of red phosphorus on the separator, which keeps the anode and cathode electrodes… Read more »
DOE funds 10 projects for lithium extraction from geothermal brines
The US Department of Energy (DOE) has announced funding of $10.9 million for 10 projects in 9 states, designed to advance innovative technologies for the extraction and conversion of battery-grade lithium derived from US geothermal brine sources. Two topic areas were chosen for the projects. The first, “Field Validation of Lithium Hydroxide Production from Geothermal… Read more »
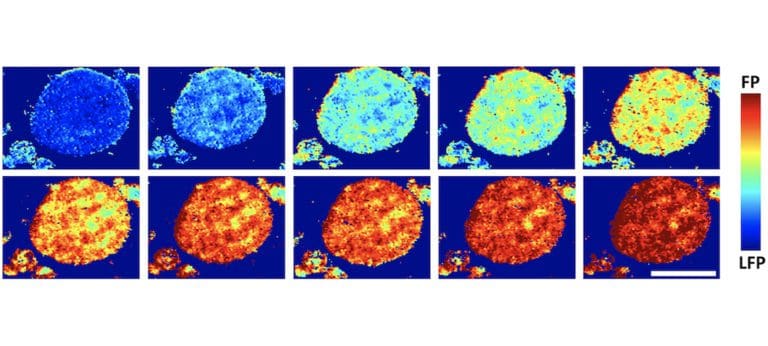
Rice researchers find misaligned crystallites in cathodes limit lithium flow
Researchers at Rice University have found that stress between misaligned crystallites in cathodes limits the flow of lithium. In an article published in ACS Energy Letters, the researchers write: “As an important battery cathode material, reaction distribution in lithium iron phosphate (LiFePO4) has been extensively studied in dispersed particle systems, but remains poorly understood for… Read more »
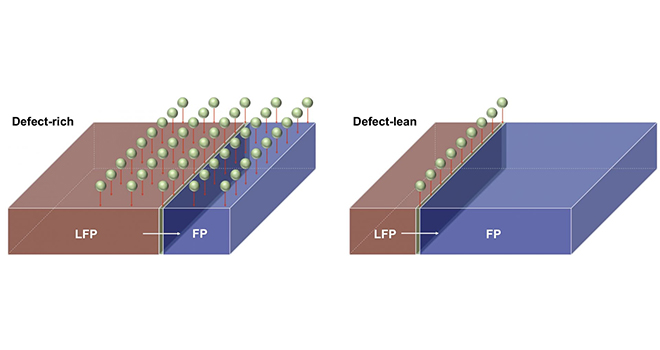
Rice researchers find inserting detours within a battery cathode improves charge/discharge rate
We have all heard the comforting bromide about our imperfections being our greatest strengths. Rice University researchers have recently proven this platitude in the context of battery charging cycles with the discovery that defects purposely inserted into the crystalline lattice of a lithium iron phosphate cathode actually cause the battery to work more, not less,… Read more »
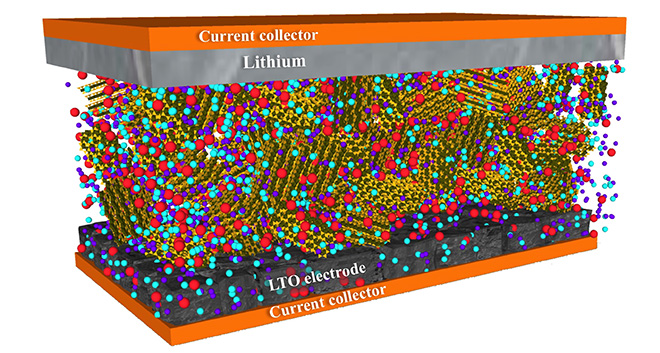
Carbon nanotubes help make lithium metal batteries more durable
Carbon nanotubes could make high-powered, fast-charging lithium metal batteries an alternative to lithium-ion batteries, according to new research from Rice University. In a paper published this month in the journal Advanced Materials, the researchers show how a carbon nanotube film can be used to keep batteries safe from dendrites, spear-like protrusions that naturally form on… Read more »
Liquid or solid-state? Clay electrolyte offers the best features of both
Bentonite clay is a malleable material with myriad applications, from oil drilling to agriculture to construction. Now researchers at Rice University have taken advantage of its qualities to develop a new class of Li-ion battery electrolytes that offer the structural stability of a solid and the wettability of a liquid. In “Quasi-Solid Electrolytes for High… Read more »
Thin-film supercapacitors could be embedded in body panels
Researchers around the world are working on supercapacitors (aka ultracaps), whose high power density makes them a perfect complement for lithium-ion batteries. Meanwhile, a couple of visionaries at Volvo have been thinking about ways to get around the high space requirements of batteries by storing energy in a car’s body panels. Image Courtesy of Volvo… Read more »
New model predicts carbon components’ performance as electrodes
Researchers at Rice University and Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory have developed a new theoretical model that predicts how carbon components will perform as electrodes. The research, published in the journal Physical Review Letters, examined the electronic characteristics of anode materials, including quantum capacitance (the ability of a material to absorb charge) and absolute Fermi level… Read more »