Sponsored by Ametek Growth in adoption of electric vehicles brings new opportunities and challenges. This is dynamic, especially in today’s climate. There are, however, some certainties: Consumers worldwide will continue to seek greener options in alignment with emerging policies. The battery pack represents a large portion of the cost associated with the EV and its… Read more »
Search Results Found For: "solid electrolyte battery"
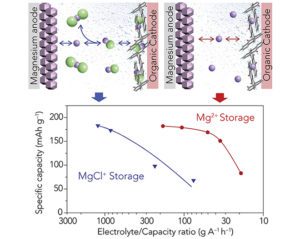
Discoveries highlight new possibilities for magnesium batteries
Magnesium batteries have long been considered a potentially safer and less expensive alternative to lithium-ion batteries, but previous versions have been severely limited in the amount of power they delivered. Researchers from the University of Houston and the Toyota Research Institute of North America (TRINA) reported in Nature Energy that they have developed a new… Read more »
Silica-based cathodes could enable long-life lithium-sulfur batteries
Scientists from the Daegu Gyeongbuk Institute of Science and Technology (DGIST) have developed a silica-based cathode for lithium-sulfur batteries, which they say could enable batteries that last for over 2,000 charge/discharge cycles. Lithium-sulfur batteries (LSBs)—composed of a sulfur-based cathode and lithium anode submerged in a liquid electrolyte—are promising candidates to replace lithium-ion batteries because of… Read more »
New Li-ion superconductor could lead to safer batteries
Researchers from the Korea Institute of Science and Technology (KIST) claim to have developed a sulfide-based superionic conductor—a material with high ion transport properties corresponding to ion conductivity of 10 to 100 mS/cm at room temperature—that can be used as a high-performance solid electrolyte in all-solid-state batteries. All-solid-state battery technology could solve the safety issues… Read more »
PNNL scientists pinpoint cause of dendrites in lithium batteries
Scientists at the DOE’s Pacific Northwest National Lab have uncovered a “root” cause of the growth of needle-like structures – known as dendrites and whiskers – that plague lithium batteries and can cause short circuit, failure, and even fire. Dendrites are tiny, rigid tree-like structures that can grow inside a lithium battery. Their needle-like projections… Read more »
Imec doubles energy density of its Li-metal batteries to 400 Wh/liter
Imec, a Belgian research firm focused on nanoelectronics, has unveiled a solid-state Li-metal battery cell with an energy density of 400 Wh/liter at a charging speed of 0.5C (2 hours). As part of a larger engineering roadmap for solid-state batteries, imec aims to surpass wet Li-ion battery performance and reach 1,000 Wh/L at 2-3C by… Read more »
BP sees big opportunities for EVs and has recently been investing in EV-related companies
The oil and gas giant’s EV investment rationale is outlined in its new report, BP Technology Outlook. Demand for travel is central to modern society. Currently, transport accounts for 20% of global primary energy use. The global light-duty fleet of cars, vans, and light trucks is here to stay for the foreseeable future. In fact,… Read more »
DOE awards $19 million for extreme fast charging research
The DOE is awarding $19 million in funding to 12 cost-shared research projects focused on “extreme fast charging,” which is defined as a system with power levels up to 400 kW and typical charging times of 15 minutes or less. Nine of the selected projects focus on advanced anodes, electrolytes, and battery cell designs: UC… Read more »
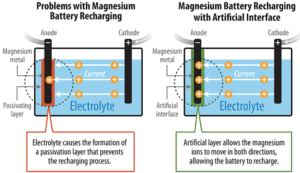
NREL scientists discover new approach for magnesium-metal batteries
Scientists at the National Renewable Energy Laboratory (NREL) have pioneered a method that enables reversible chemistry of magnesium metal in noncorrosive carbonate-based electrolytes. The technology has several potential advantages over lithium-ion batteries, including higher energy density, improved stability and lower cost. Magnesium batteries can theoretically store almost twice as much energy per volume as lithium-ion… Read more »
Waterloo team develops low-cost approach to stabilize lithium metal anodes
Researchers at the University of Waterloo in Canada have developed a way to stabilize lithium metal electrodes by forming a single-ion-conducting and stable protective surface layer in vivo. In “An In Vivo Formed Solid Electrolyte Surface Layer Enables Stable Plating of Li Metal,” published in the journal Joule, Quan Pang, Xiao Liang and colleagues explain how they… Read more »