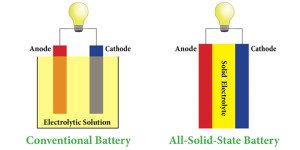
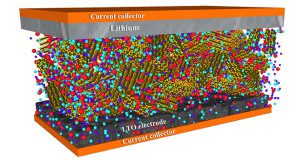
Researchers led by a team from China’s Ningbo Institute of Materials Technology and Engineering have developed stable solid-state lithium batteries with high energy and power densities. In “High-Energy All-Solid-State Lithium Batteries with Ultralong Cycle Life,” published in Nano Letters, the scientists explain how they developed a new interfacial architecture. They say that their design approach… Read more »
Search Results Found For: "solid electrolyte battery"
Is improved formation cycling the key to lower battery costs?
European conglomerate thyssenkrupp, BMW and several other firms and research institutions are collaborating on a project called EffiForm, which aims to make a detailed study of the solid electrolyte interface (SEI) layer formation process in Li-ion batteries. While the ins and outs of forming an SEI layer may seem arcane, in fact there’s a highly practical… Read more »
A closer look at electrolytes in advanced batteries
The electrolytes in advanced batteries are based on incredibly complicated formulations. If you calculated all of the possible combinations of solvents, salts and additives while trying to find the optimal ratios for just one electrolyte formulation, it would add up to an extraordinary number of possibilities. Because it plays such a critical role in battery… Read more »
New electrolyte for solid-state batteries combines polymer and glass
Scientists at the DOE’s Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory have developed a novel electrolyte that addresses many of the problems of solid electrolytes by combining the two primary types – polymer and glass. There are two kinds of solid electrolytes – polymer and glass or ceramic – and each has its own set of challenges. Polymer… Read more »
Hitachi researchers demonstrate thermally durable solid-state Li-ion battery
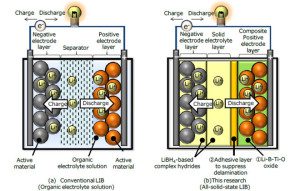
A research team sponsored by Hitachi and Tohoku University’s Advanced Institute for Material Research (AIMR) has demonstrated technology that reduces the internal resistance of all-solid-state Li-ion batteries through the use of LiBH4-based complex hydrides as solid electrolytes. A conventional Li-ion battery uses a volatile organic electrolyte solution with a maximum operating temperature around 60˚ C…. Read more »
Water-in-salt electrolyte could enable high-voltage aqueous Li-ion chemistries
A team of researchers from the University of Maryland (UMD) and the US Army Research Laboratory (ARL) have devised what they call a “water-in-salt” electrolyte that could offer power, efficiency and longevity comparable to Li-ion batteries, but without the toxic chemicals and fire risk. In “Water-in-salt electrolyte enables high-voltage aqueous lithium-ion chemistries,” published in the… Read more »
Liquid or solid-state? Clay electrolyte offers the best features of both
Bentonite clay is a malleable material with myriad applications, from oil drilling to agriculture to construction. Now researchers at Rice University have taken advantage of its qualities to develop a new class of Li-ion battery electrolytes that offer the structural stability of a solid and the wettability of a liquid. In “Quasi-Solid Electrolytes for High… Read more »
Tesla tweaks its battery chemistry: a closer look at silicon anode development
In mid-July, Tesla Motors made a trio of Model S update announcements. The new options included a 70 kWh rear-wheel-drive base model, an upgrade for the high-end battery pack from 85 to 90 kWh (providing about a 6% increase in range), and Ludicrous mode, which offers a 10% improvement in the car’s 0 to 60… Read more »
Solid-state battery innovator Seeo acquired by Bosch
Giant German automotive supplier Bosch has announced that it will acquire the Silicon Valley startup Seeo, a pioneer in solid-state battery technology. Seeo’s cell design combines a solid lithium metal anode with a conventional porous lithium iron phosphate cathode and Seeo’s proprietary DryLite solid polymer electrolyte. Seeo says its cells achieve specific energy of around… Read more »
Researchers add compounds to electrolyte to prevent dendrite growth
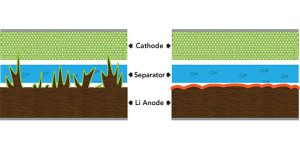
Those doggone dendrites are the bane of battery boffins working on otherwise promising lithium metal anodes. Now a group of researchers from SLAC, Stanford and MIT have discovered that adding lithium polysulfide and lithium nitrate to an ether-based electrolyte can prevent dendrite growth and minimize electrolyte decomposition. Professor Yi Cui, Professor Yet-Min Chiang (a co-founder… Read more »