Here’s a treat for any EV fan: a long and meaty talk with Tesla founders Martin Eberhard and Marc Tarpenning, delivered at Stanford last October. While there are several substantial talks with Tarpenning available on YouTube (he also graciously granted me a lengthy interview for my book about Tesla), Martin Eberhard has seldom sat down… Read more »
Search Results Found For: "stanford"
Researchers demonstrate Li-ion anode with silicon-nanolayer-embedded graphite/carbon
Larger figure Researchers from South Korea’s Ulsan National Institute of Science and Technology (UNIST) and Stanford University have demonstrated the feasibility of a hybrid anode for Li-ion batteries using silicon-nanolayer-embedded graphite/carbon. In “Scalable synthesis of silicon-nanolayer-embedded graphite for high-energy lithium-ion batteries,” published in Nature Energy, Minseong Ko and colleagues explain that this architecture allows compatibility… Read more »
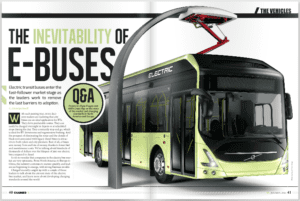
The inevitability of electric buses
Electric transit buses enter the fast-follower market stage as the leaders work to remove the last barriers to adoption. Q&A with Proterra’s Ryan Popple and ABB’s Daan Nap on the state of the market and charging standards in North America and Europe. With each passing year, more decision makers are realizing that city buses are an… Read more »
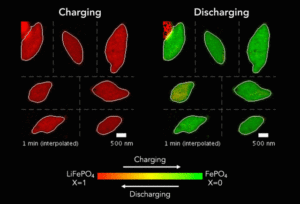
New X-ray microscopy technique reveals the secret life of batteries
In pursuit of their quest for more capable batteries, scientists are searching for better ways to observe battery particles as they charge and discharge in real time. A new technique developed at Berkeley Lab’s Advanced Light Source is providing researchers with nanoscale images of the electrochemical reactions that make lithium-ion batteries do their thing. In… Read more »
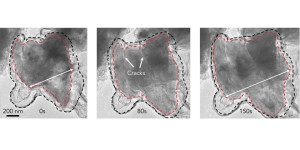
Graphene cages could be the key to silicon anodes
Battery boffins are buzzing about silicon anodes, which could store up to 10 times more energy than today’s anodes. The catch is that silicon particles tend to swell and crack during cycling, and to react with the electrolyte in unwanted ways. Now a team from Stanford University and the Department of Energy’s SLAC National Accelerator… Read more »
Two-level cathode structure improves battery performance
As the search for a better battery grinds on, a lot of the attention is focused on potential cathode materials. Nickel is one possibility that shows a lot of promise – its drawback is that it is unstable and tends to have destructive reactions with the electrolyte. Now a team of scientists from the Brookhaven… Read more »
New material shuts down batteries at high temperatures and restarts when it cools
Stanford researchers have invented a new technology that could eliminate thermal runaway in high-energy-density batteries. Thermal runaway refers to a chain reaction in which an increase in temperature causes further increases in temperature and uncontrollable release of energy. In “Fast and reversible thermoresponsive polymer switching materials for safer batteries,” published in Nature Energy, Professor Zhenan Bao and… Read more »
Paraclete Energy says its low-cost silicon nanoparticles can at least double your current anode capacity
Silicon has a theoretical charge capacity ten times higher than typical graphite. That is why a mind-blowing number of researchers are working towards replacing more and more of the graphite used in today’s lithium-ion battery anodes with silicon. In the last issue of Charged, we discussed Tesla’s announcement that it had begun to use small… Read more »
Silicon Valley’s Motiv helps electrify heavy-duty trucks, shuttles and buses
Sometimes kids can’t wait to be grown-ups, but growth takes time. An acorn doesn’t become an oak tree overnight. Electric vehicles are a growth industry, and many people in that industry would like to see explosive expansion, rather than the slow and steady gains that have characterized the market for years. Yet even slow progress… Read more »
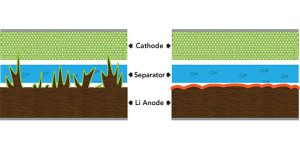
Researchers add compounds to electrolyte to prevent dendrite growth
Those doggone dendrites are the bane of battery boffins working on otherwise promising lithium metal anodes. Now a group of researchers from SLAC, Stanford and MIT have discovered that adding lithium polysulfide and lithium nitrate to an ether-based electrolyte can prevent dendrite growth and minimize electrolyte decomposition. Professor Yi Cui, Professor Yet-Min Chiang (a co-founder… Read more »